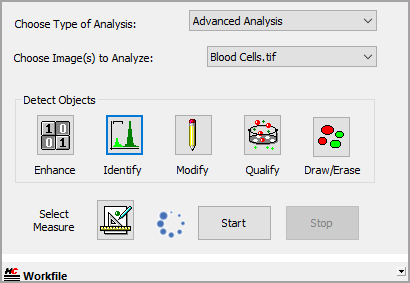
What is a Workfile? A Workfile is a simplified icon driven macro available in HCImage Analysis. It easily automates repetitive tasks while allowing supervision and correction of specific processes. Select Advanced Analysis to open the Workfile panel.
A sequential series of tasks are created and stored using the icons in the Tools panel and saved with the extension .enh as a workfile.

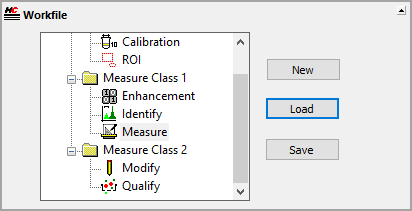
The measurement algorithm is set up by configuring an icon-driven workfile (macro), by adding steps in an interactive process and observing the effects on the identified image objects as the various steps are added and modified. The procedure is methodical, where the operator selects each option interactively. The steps used can be saved in a workfile (macro) for later reuse, review, or modification.
The Detect Objects pane contains task specific icons used to collect data from images. The icons may be used to build a Workfile for later use or individually (manually) on an image or data document. The icon layout follows the typical order of steps used in collecting object measurements, although not every icon has to be used.
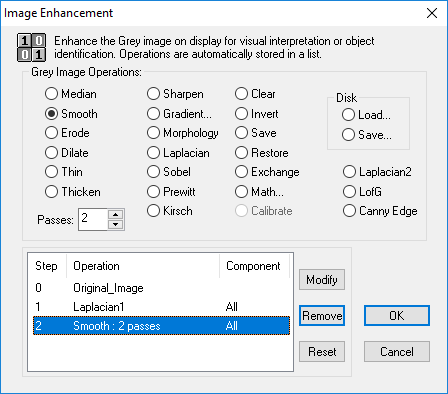
Enhance is used to optimize images by removing defects and imperfections that make object identification very difficult. Use a combination of enhance operations such as Convolutions![]() In manipulating an image with a digital image processor, the substitution of the grey value of each pixel with another grey value that takes into account the values of neighboring pixels. The convolution mask or kernel used to calculate the influence of the neighbors determines the degree to which the picture is sharpened or smoothed by the convolution process. This contrasts with a point operation, where the grey value of each pixel is transformed without considering the neighbors.
A group of pixels called a kernel is compared against other pixels and the mathmatical result is placed in the center of the kernel., Edge Operators
In manipulating an image with a digital image processor, the substitution of the grey value of each pixel with another grey value that takes into account the values of neighboring pixels. The convolution mask or kernel used to calculate the influence of the neighbors determines the degree to which the picture is sharpened or smoothed by the convolution process. This contrasts with a point operation, where the grey value of each pixel is transformed without considering the neighbors.
A group of pixels called a kernel is compared against other pixels and the mathmatical result is placed in the center of the kernel., Edge Operators![]() Enhances object boundaries for detection and measurements. and Image Arithmetic
Enhances object boundaries for detection and measurements. and Image Arithmetic![]() Arithmetically combine the current image with the saved image. when dealing with complex image structures. For more information on image enhancements see "Enhance Overview."
Arithmetically combine the current image with the saved image. when dealing with complex image structures. For more information on image enhancements see "Enhance Overview."
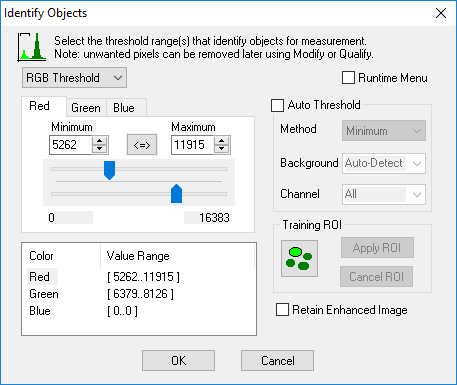
The Identify dialog box controls the way that a binary image is created for later editing, modification and measurement. This is done using a technique called Thresholding![]() The maximum and minimum values for a range of grayscale intensities, to be used for segmentation of an image. (See also Segmentation) or Segmentation. The binary image is a map of all detected pixels that may later be combined together into objects for measurement. For information on object identification see "Identify Overview."
The maximum and minimum values for a range of grayscale intensities, to be used for segmentation of an image. (See also Segmentation) or Segmentation. The binary image is a map of all detected pixels that may later be combined together into objects for measurement. For information on object identification see "Identify Overview."
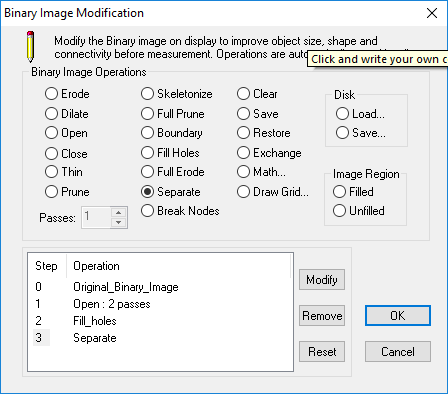
Once the binary image has been created, use Modify (short for Binary Image Modification) to improve object size, shape and connectivity or combine with other binary images. The goal is to improve the binary image for better object measurements. Create a combination of operations, edit or remove, save and load binary layers from memory and disk using the Modify dialog. For more information about modifying the binary image layer see "Modify Overview."
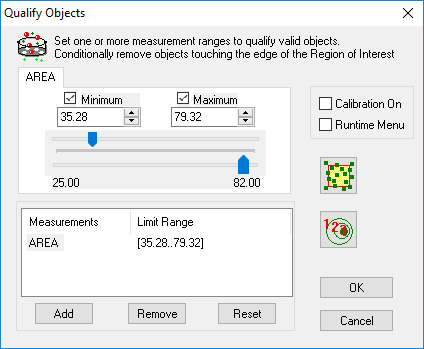
Qualify allows another level of refinement and provides the means to filter selected objects from the binary image for inclusion in a measured dataset. Qualify compares object populations against one or more qualification criteria as a type of filtering system to reject various objects based on size, shape, intensity or position. For more information about removing objects based on physical characteristics see "Qualify Overview."
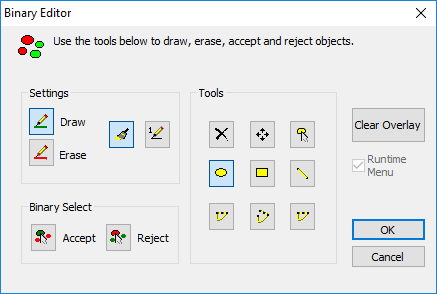
Sometimes there is a need to manually edit the binary image. The Binary Editor is a great tool that provides precision, accuracy and a variety of tools for editing objects. For more information about editing binary images see "The Binary Editor (Draw/Erase)."
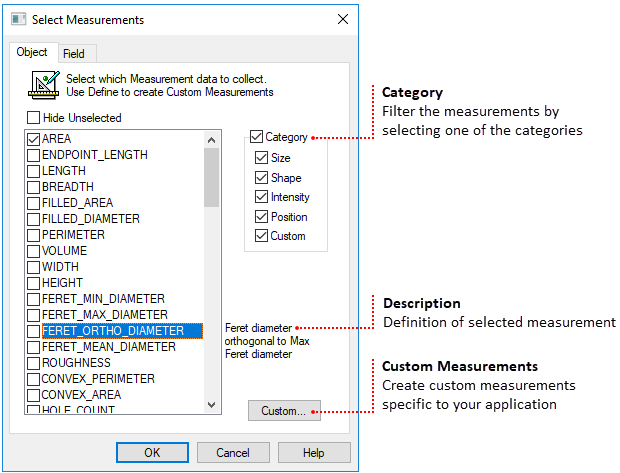
Once all of the objects of interest have been identified use Measure to select which object and field measurements to collect. There are over 150 size, shape, intensity and position measurements to choose from. For specialized measurements create custom measurements with the built-in equation editor.
In order to make Object Measurements, the pixels detected in the Binary image must be related together as object. This is done by object detection techniques, one technique is called Labeling, where every pixel belonging to the same object is given a value, and every object has a different value. Another technique used is boundary tracing to identify characteristics of an object based on shape. The measurement algorithms can then compute the measurements selected for each object, and store them for statistical analysis.